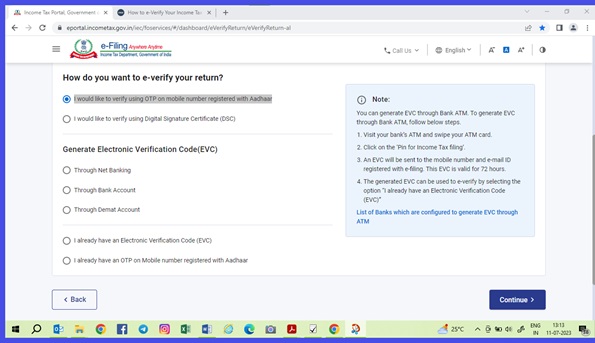
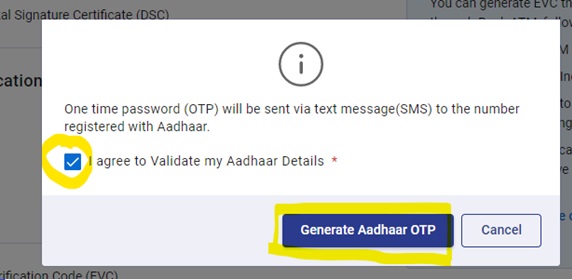
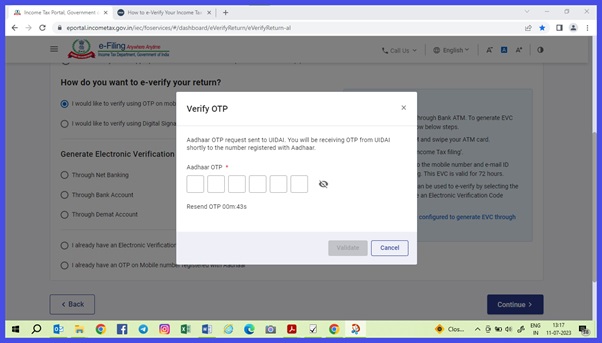
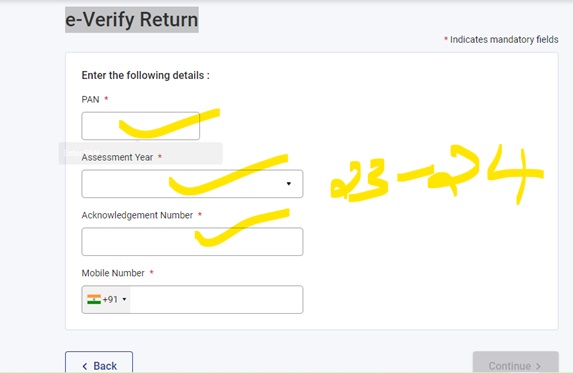
| Nature of Payment | Basic Cut off (Rs) | Individual /Company and others New Rate %) | If No Pan or Invalid PAN (Rate %) |
| 192 – Salaries | Slab Rate | Slab Rates | 30% |
| 192A- Premature withdrawal from Employee Provident Fund (Note 1) | 50,000 | Individual: 10% Company: NA | 20% |
| 193 – Interest on securities (Note 2 & 3) | 2,500 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194 – Dividend other than the dividend as referred to in Section 115-O | 5,000 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194A – Interest other than interest on securities – Banks Time deposits, Recurring deposit and Deposit in Co-op Banks (Note 3) | 40,000 (for individual) 50000 (for Senior Citizens) | Individual: 10% | 20% |
| 194B – Winning from Lotteries | 10,000 | Individual: 30% Company: 30% | 30% |
| 194BA – Winnings from Online Gaming (Note 16) | Amount of net winnings comprised
in withdrawal | Individual: 30% Company: 30% | 30% |
| 194BB – Winnings from Horse Race | 10,000 | Individual: 30% Company: 30% | 30% |
| 194C- Payment to Contractor – Single Transaction (Note 4) | 30,000 | Individual: 1% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194C-Payment to Contractor – Aggregate During the Financial year (Note 4) | 1,00,000 | Individual: 1% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194C- Contract – Transporter not covered under 44AE (Note 4) | 30,000 / 75,000 | Individual: 1% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194C- Contract – Transporter covered under 44AE & submit declaration on prescribed form with PAN | – | – | 20% |
| 194D – Insurance Commission | 15,000 | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194DA Payment in respect of life insurance policy (Note 5) | 1,00,000 | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194E – Payment to Non-Resident Sportsmen or Sports Association | – | Individual: 20% Company: 20% | 20% |
| 194EE – Payments out of deposits under National Savings Scheme | 2,500 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194F – Repurchase Units by MFs | – | Individual: 20% Company: 20% | 20% |
| 194G – Commission – Lottery | 15,000 | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194H – Commission / Brokerage | 15,000 | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194I – Rent – Land and Building – furniture – fittings | 2,40,000 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194I – Rent – Plant / Machinery / equipment | 2,40,000 | Individual: 2% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194IA -Transfer of certain immovable property other than agriculture land | 50,00,000 | Individual: 1% Company: 1% | 20% |
| 194IB – Rent – Land or building or both | 50,000 per month | Individual: 5% | 20% |
| 194IC – Payment of Monetary consideration under Joint development agreement | – | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194J – Professional Fees for technical services (w.e.f. from 1.4.2020) (Note 6) | 30,000 | Individual: 2% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194J – Professional Fees in all other cases | 30,000 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194K- Payment of any income in respect of Units of Mutual fund as per section 10(23D) or Units of administrator or from a specified company (Note 7) | – | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194LA – TDS on compensation for compulsory acquisition of immovable Property (Note 8) | 2,50,000 | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194 LBA (1)- Business trust shall deduct tax while distributing, any interest received or receivable by it from a SPV or any income received from renting or leasing or letting out any real estate asset owned directly by it, to its unit holders. (Note 9) | | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 194LB – Income by way of interest from infrastructure debt fund (non-resident) | – | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194LBB – Income in respect of investment in Securitisation trust. | – | Individual: 10% Company: 30% | 30% |
| 194LBC- Income in respect of investment made in a securitisation trust | – | Individual: 25% Company: 30% | 30% |
| 194 LC – Income by way of interest by an Indian specified company to a non-resident / foreign company on foreign currency approved loan / long-term infrastructure bonds from outside India (Note 10) | – | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194LD – Interest on certain bonds and govt. Securities (Note 11) | – | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194M – Payment of Commission, brokerage, contractual fee, professional fee to a resident person by an Individual or a HUF who are not liable to deduct TDS under section 194C, 194H, or 194J. | 50,00,000 | Individual: 5% Company: 5% | 20% |
| 194N – Cash withdrawal in excess of Rs. 20 Lakh during the previous year from one or more account maintained by a person with a banking company, co-operative society engaged in business of banking or a post office. | 20,00,000 | Individual: 2% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194N – Cash withdrawal in excess of Rs. 1 crore during the previous year from one or more account maintained by a person with a banking company, co-operative society engaged in business of banking or a post office. (Note 12) | 100,00,000 | Individual: 2% Company: 2% | 20% |
| 194N – Cash withdrawal in excess of Rs. 3 crore during the previous year from one or more account maintained by a Co operative society with a banking company, co-operative society engaged in business of banking or a post office. (Note 15) | 300,00,000 | Co-operative Society : 5% | 20% |
| 194O – Applicable for E-Commerce operator for sale of goods or provision of service facilitated by it through its digital or electronic facility or platform. | – | Individual: 1% Company: 1% | 20% |
| 194P- TDS by specified bank to specified senior citizen | – | Rates applicable to particular slab of income including applicable Surcharge and Health & Education Cess | |
| 194Q- Purchase of goods | 50,00,000 | 0.1% | |
| 194R- Deduction of tax on benefit of perquisite in respect of business or profession | Resident Indiviual: 20,000 | 10% | |
| 194S- Transfer of a virtual digital asset | Resident Individual & HUF: 50,000
Others: 10,000 | 1% | |
| 195- Payment of any sum to Non resident | – | – | Higher of Rate in force or Double Taxation Avoidance Act rate |
| 196B – Income from units | – | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 196C-Income from foreign currency bonds or GDR (including long-term capital gains on transfer of such bonds) (not being dividend) | – | Individual: 10% Company: 10% | 20% |
| 196D – Income of FIIs from securities | – | Individual: 20% Company: 20% | 20% |